1. 함수 포인터
#include <stdio.h>
void SimpleAdder(int n1, int n2)
{
printf("%d + %d = %d \n", n1, n2, n1+n2);
}
void ShowString( char *str)
{
printf("%s \n", str);
}
int main()
{
char *str = "Function ptr";
int num1=10, num2=20;
void (*fptr1)(int, int) = SimpleAdder;
void (*fptr2)(char *) = ShowString;
fptr1(num1, num2);
fptr2(str);
}
#include <stdio.h>
int WhoIsFirst(int age1, int age2, int (*cmp)(int n1, int n2))
{
return cmp(age1, age2);
}
int OlderFirst(int age1, int age2)
{
if (age1>age2)
return age1;
else if (age1 < age2)
return age2;
else
return 0;
}
int YoungerFirst(int age1, int age2)
{
if (age1< age2)
return age1;
else if (age1 > age2)
return age2;
else
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int age1=20;
int age2=30;
int first;
printf("입장순서 1 \n");
first = WhoIsFirst(age1, age2, OlderFirst);
printf("%d세와 %d세 중 %d세가 먼저 입장!! \n\n", age1, age2, first);
printf("입장순서 2 \n");
first = WhoIsFirst(age1, age2, YoungerFirst);
printf("%d세와 %d세 중 %d세가 먼저 입장! \n\n", age1, age2, first);
}
#include <stdio.h>
void SoSimpleFunc(void)
{
printf("I'm so simple");
}
int main()
{
int num=20;
void *ptr; // void* 포인터 변수 함수 담을 수 있따.
ptr = #
printf("%p \n", ptr);
ptr = SoSimpleFunc;
printf("%p \n", ptr);
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i = 0;
printf("전달된 문자열 수 : %d\n", argc);
for(i=0; i<argc; i++)
printf("%d 번째 문자열 : %s \n", i + 1, argv[i]);
}
2. 문자 스트림
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int ch;
while(1)
{
ch = getchar();
if ( ch ==EOF)
break;
putchar(ch);
}
}#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char *str = "simple string";
printf("1. puts test ----\n");
puts(str);
puts("so simple string");
printf("2. fputs test ----\n");
fputs(str, stdout);
printf("\n");
printf("so simple string", stdout);
printf("\n");
printf("3. end of main ----\n");
}#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char perID[7];
char name[10];
fputs("주민번호 앞 6자리 입력 : ", stdout);
fgets(perID, sizeof(perID), stdin);
//6자리 입력시 fgets는 \n까지 읽고, \n이 남음
// -> 나머지 fgets에서도 버퍼에 남은 \n에 바로 종료되어 입력 못함
fputs("이름 입력 : ", stdout);
fgets(name, sizeof(name), stdin);
printf("주민번호 : %s \n", perID);
printf("이름 : %s \n", name);
}#include <stdio.h>
void ClearLineFromReadBuffer()
{
while(getchar() != '\n');
}
int main()
{
char perID[7];
char name[10];
fputs("주민번호 앞 6자리 입력 : ", stdout);
fgets(perID, sizeof(perID), stdin);
//getchar()로 버퍼내 \n를 읽으면 무한루프 탈출!, 버퍼가 비워짐.
ClearLineFromReadBuffer();
fputs("이름 입력 : ", stdout);
fgets(name, sizeof(name), stdin);
printf("주민번호 : %s \n", perID);
printf("이름 : %s \n", name);
}
3. 구조체 1

#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
struct point
{
int xpos;
int ypos;
};
int main()
{
struct point pos1, pos2;
double distance;
fputs("point1 pos : ", stdout);
scanf("%d %d", &pos1.xpos, &pos2.ypos);
fputs("point2 pos : ", stdout);
scanf("%d %d", &pos2.xpos, &pos2.ypos);
distance = sqrt((double)((pos1.xpos - pos2.xpos) *
(pos1.xpos - pos2.xpos) + (pos1.ypos-pos2.ypos) * (pos1.ypos-pos2.ypos)));
printf("두 점의 거리는 %g 입니다~\n", distance);
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct person
{
char name[20];
char phoneNum[20];
int age;
};
int main()
{
struct person man1, man2;
strcpy(man1.name, "무야호");
strcpy(man1.phoneNum, "010-1544-7676");
man1.age = 23;
printf("이름 입력 : ");
scanf("%s", man2.name);
printf("번호 입력 : ");
scanf("%s", man2.phoneNum);
printf("나이 입력 : ");
scanf("%d", &(man2.age));
printf("이름 : %s \n", man1.name);
printf("번호 : %s \n", man1.phoneNum);
printf("나이 : %d \n", man1.age);
printf("이름 : %s \n", man2.name);
printf("번호 : %s \n", man2.phoneNum);
printf("나이 : %d \n", man2.age);
}
#include <stdio.h>
struct point
{
int xpos;
int ypos;
};
struct person
{
char name[20];
char phoneNum[20];
int age;
};
int main(void)
{
struct point pos = {10, 20};
struct person man = {"이승기", "010-1234-5678", 21};
printf("%d %d \n", pos.xpos, pos.ypos);
printf("%s %s %d \n", man.name, man.phoneNum, man.age);
}
#include <stdio.h>
//struct arr
struct point
{
int xpos;
int ypos;
};
int main()
{
struct point arr[3];
int i;
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
printf("점의 좌표 입력 : ");
scanf("%d %d", &arr[i].xpos, &arr[i].ypos);
}
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++)
printf("[%d %d] ", arr[i].xpos, arr[i].ypos);
}
#include <stdio.h>
//init struct array
struct person
{
char name[20];
char phoneNum[20];
int age;
};
int main()
{
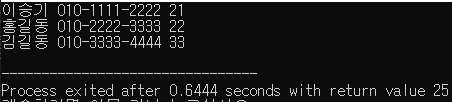
struct person arr[3] = {
{"이승기", "010-1111-2222", 21},
{"홍길동", "010-2222-3333",22},
{"김길동", "010-3333-4444",33}
};
int i;
for(i=0;i<3; i++)
printf("%s %s %d \n", arr[i].name, arr[i].phoneNum, arr[i].age);
}
#include <stdio.h>
struct point
{
int xpos;
int ypos;
};
struct circle
{
double radius;
struct point * center;
};
int main(){
struct point cen = {2, 7};
double rad = 5.5;
struct circle ring = {rad, &cen};
printf("원의 반지름 : %g \n", ring.radius);
printf("원의 중심 [%d, %d] \n", (ring.center) -> xpos, (ring.center) ->ypos);
}
#include <stdio.h>
struct point
{
int xpos;
int ypos;
struct point *ptr;
};
int main(void)
{
struct point pos1 = {1, 1};
struct point pos2 = {2, 2};
struct point pos3 = {3, 3};
pos1.ptr = &pos2;
pos2.ptr = &pos3;
pos3.ptr = &pos1;
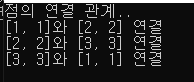
printf("점의 연결 관계.. \n");
printf("[%d, %d]와 [%d, %d] 연결 \n",
pos1.xpos, pos1.ypos, pos1.ptr->xpos, pos1.ptr->ypos);
printf("[%d, %d]와 [%d, %d] 연결 \n",
pos2.xpos, pos2.ypos, pos2.ptr->xpos, pos2.ptr->ypos);
printf("[%d, %d]와 [%d, %d] 연결 \n",
pos3.xpos, pos3.ypos, pos3.ptr->xpos, pos3.ptr->ypos);
}
'컴퓨터과학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| MINT64OS - 1. 시작 및 개발환경 구축 삽질기 (0) | 2022.07.04 |
|---|---|
| 프로그래밍연습 - 2.[C] 구조체 2, 동적할당, 전처리, 파일 분할 (0) | 2022.06.21 |
| 리눅스 프로그래밍 4 - 메모리, 프로세스, 시그널, 환경, 로그인 (0) | 2022.06.01 |
| 리눅스 프로그래밍 3 - grep 구현, 리눅스 디렉터리구조, 파일시스템관련 명령어 구현 (0) | 2022.05.31 |
| 리눅스 프로그래밍 2 - stdio, head 구현, gdb 디버깅 (0) | 2022.05.31 |