지난주 페이스 무너지고 나서 제대로 못하고 있었는데
드뎌 mpu6050 다뤄보려고함
기존에 이미 아두이노 mpu6050 사용하는 글들 많은데
무엇을 참고할가..
한참 찾은건 아니지만
이 링크에서 데이터 시트 참고해서 설명을 해주고 있고,
[MPU6050] 1. 데이터 시트를 통해 센서 값 확인하기
구글에 MPU6050 데이터 시트를 검색하면 다음과 같은 파일을 찾을 수 있다. 최상단의 파일은 말 그대로 데이터 시트로 센서에 관한 스펙과 통신 방식, 전력 등에 관한 것을 제조사에서 정리한 것이
chigun.tistory.com
이 글에서는 mpu6050 lib로 ypr 를 뽑아내는 예제를 보여준다.
https://m.blog.naver.com/boilmint7/220932352810
아두이노 3축자이로센서(MPU-6050)사용 예제설명
아두이노 3축자이로센서(MPU-6050) 사용 예제 설명. 아두이노 자이로센서 (MPU-6050) ...
blog.naver.com
mpu6050에서 바로 rpy 뽑아내는것도 좋지만
그래도 쓰는데 데이터시트 내용 대충 한번 보긴해야겠지
글을 찾아보니 mpu6050을 아두이노 핀 a4, a5에 연결해야한다고하는데
i2c 통신하면 디지털쪽해야하지 않나 싶다가
이게 우노에서 i2c 통신에 사용되는 핀이라고한다.
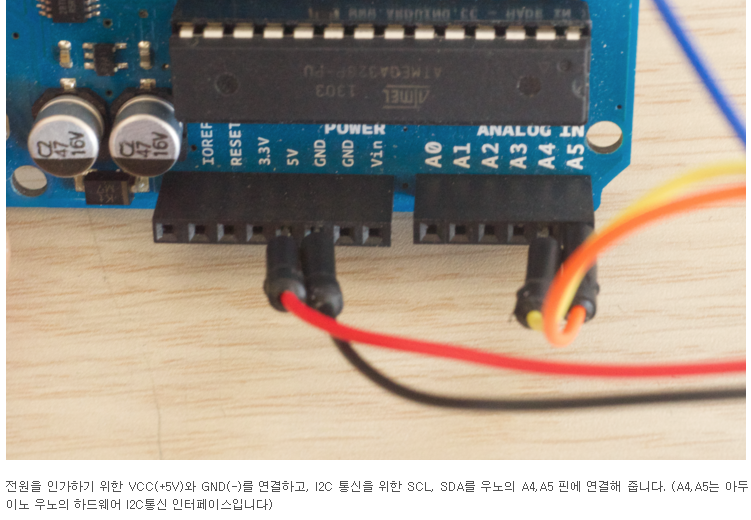

우노보드 핀맵을 열어보면 a4, a5가 sda, scl이 맞긴하다.
시키는데로 연결하고
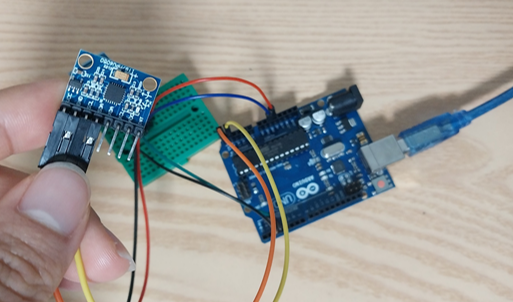
[MPU6050] 1. 데이터 시트를 통해 센서 값 확인하기
구글에 MPU6050 데이터 시트를 검색하면 다음과 같은 파일을 찾을 수 있다. 최상단의 파일은 말 그대로 데이터 시트로 센서에 관한 스펙과 통신 방식, 전력 등에 관한 것을 제조사에서 정리한 것이
chigun.tistory.com
다시 이 링크로 돌아와 글을보는데 정리하면 이런듯
1. 아두이노 i2c 통신을 하려면 wire.h 사용
2. mpu6050 ic2 주소값은 0x68
3. mpu6050 초기화 : 0x68에다가 107, 0 송신 : 107레지스터에 0 전달
* 초기화 해주면 다시는 안해도됨.
4. 뒷 내용은 각가속도 중력가속도 감도 설정 + 레지스터에서 값가져오기
내용은 완벽히 이해하긴 힘들지만
그래도 데이터시트랑 i2c 읽어오는 내용을 꽤 친절하게 설명해주니 이만큼 봐도 충분해보임.
하지만 나는 각가속도, 중력가속도가 아니라 rpy가 필요해서
이제 다른글 보고진행
하기전에
i2c 주소값이 0x68이면
나는 mpu 6050여러개 쓸건데 어떻게하면 되나 궁금해짐
gpt에게 물어봄
q : 아두이노 우노보드에서 mpu6050 2개를 사용하려면 어떻게 작성하면되 mpu6050의 i2c 주소값은 0x68이라고하는데, 두개다 주소가 같은거아니야?
a : 아뇨, MPU6050 모듈은 I2C 통신을 통해 통신하는데, 주소를 변경하여 같은 버스 상에 여러 개의 모듈을 사용할 수 있습니다. 보통 MPU6050의 기본 주소는 0x68이지만, AD0 핀의 상태에 따라(AD0 핀이 GND에 연결되면 0x68, VCC에 연결되면 0x69) 주소를 변경할 수 있습니다. 두 개의 MPU6050 모듈을 사용할 때, 하나는 0x68 주소로 설정하고 다른 하나는 0x69 주소로 설정하여 충돌을 피할 수 있습니다.
q : 그러면 2개가 아니라 mpu6050을 5개 사용하는 경우 어떻게 하면되
a : 만약 MPU6050을 5개 사용하려면, 각각의 모듈에 고유한 I2C 주소를 할당해야 합니다. MPU6050 모듈은 AD0 핀을 통해 주소를 변경할 수 있습니다. AD0 핀을 다른 GPIO 핀에 연결하고 해당 핀을 사용하여 AD0 핀을 제어하여 주소를 변경할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 5개의 MPU6050 모듈을 사용하는 경우, 각 모듈에 다른 주소를 할당하기 위해 AD0 핀을 5개의 GPIO 핀에 연결하고, 해당 GPIO 핀을 사용하여 AD0 핀을 제어하여 주소를 변경할 수 있습니다. 이렇게 하면 각 MPU6050 모듈은 고유한 주소를 가지게 됩니다.
대충 얘 설명이 맞는지는 몰라도 mpu6050에 있는 ad0핀으로 mpu6050 여러개쓸때 고유 주소갖도록 변경할수 있나봄.
비트연산으로 값뽑아오는건 여기서 꽤 친절하게 설명해준편
https://steemit.com/kr-arduino/@codingman/mpu-6050
MPU-6050 가속도/자이로 센서 제어 (아두이노) — Steemit
MPU-6050 가속도/자이로 센서 제어 (아두이노) 오늘은 MPU-6050 가속도/자이로 센서를 이용하여 실험하는 시간을 갖도록 하겠습니다. 자이로 센서를 사용하려면 오일러의 공식을 알아야 하고 오일러
steemit.com
다시 돌아와 rpy뽑아내는 링크 참고
https://m.blog.naver.com/boilmint7/220932352810
아두이노 3축자이로센서(MPU-6050)사용 예제설명
아두이노 3축자이로센서(MPU-6050) 사용 예제 설명. 아두이노 자이로센서 (MPU-6050) ...
blog.naver.com
근데 위 글에서는 INT 핀을 D2와 연결해야된다고 한다.
gpt 한태 물어봄
q : 아두이노 우노보드 mpu6050 사용하는 글 찾아봤는데 INT핀을 D2와 연결시키던데 이건왜하는거야? SCL, SDA만 연결해도 되지않아?
a : INT 핀을 D2에 연결하는 이유는 MPU6050의 인터럽트 기능을 사용하기 위함입니다. 이를 통해 특정 조건이 충족되었을 때 인터럽트를 발생시키고 처리할 수 있습니다. SCL과 SDA는 데이터 통신을 위한 핀이며, INT 핀은 MPU6050의 상태를 감지하고 처리하는 데 사용됩니다. 따라서 INT 핀을 D2와 연결하여 MPU6050의 인터럽트를 사용할 수 있습니다.
제대로 찾아본건 아니지만 국내 블로그 글에서는 int핀을 사용하는 이유를 제대로 설명하진 않고있다.
mpu6050 라이브러리에서 쓰나보지 싶어 그냥 나는 D4에 연결
(블루투스로 D2,D3 쓰고있기 때문)
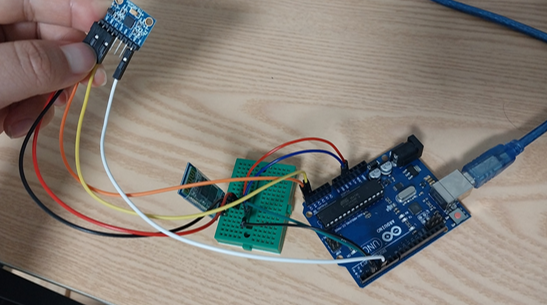
이 글에서 시키는데로 라이브러리 다운받으려고하는데
첨부파일 다운이안된다.
대신 여기서 다운받아 사용
https://bella1130.tistory.com/35
[17] 자이로 센서(MPU 6050)
자이로센서의 움직임을 시각적으로 보여주는 processing이라는 툴을 사용해 보도록 하겠습니다. 아두이노, 자이로센서의 연결은 다음과 같습니다. 여기에서 실행할 프로그램은 arduino의 인터럽
bella1130.tistory.com
원 블로그글 링크대로가면
C:\Program Files (x86)\Arduino\libraries
여기가면 된다는데
나는 아두이노 라이브러리가
앱데이터 로컬쪽에 가있더라.
C:\Users\jdo\AppData\Local\Arduino15\libraries
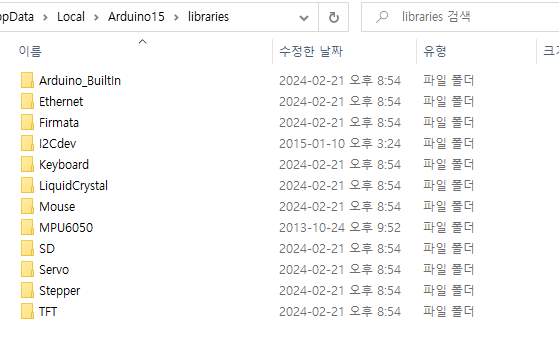
근데 여기다 추가하고 아두이노 ide를 열어도 예제가 추가되질 않는다.
아무 예제나 열어서 폴더 열기해보니까
임시폴더에 들어가있더라
그냥 아쉬운데로 mpu6050 내 dmp 예제 열어봣는데
// I2C device class (I2Cdev) demonstration Arduino sketch for MPU6050 class using DMP (MotionApps v2.0)
// 6/21/2012 by Jeff Rowberg <jeff@rowberg.net>
// Updates should (hopefully) always be available at https://github.com/jrowberg/i2cdevlib
//
// Changelog:
// 2013-05-08 - added seamless Fastwire support
// - added note about gyro calibration
// 2012-06-21 - added note about Arduino 1.0.1 + Leonardo compatibility error
// 2012-06-20 - improved FIFO overflow handling and simplified read process
// 2012-06-19 - completely rearranged DMP initialization code and simplification
// 2012-06-13 - pull gyro and accel data from FIFO packet instead of reading directly
// 2012-06-09 - fix broken FIFO read sequence and change interrupt detection to RISING
// 2012-06-05 - add gravity-compensated initial reference frame acceleration output
// - add 3D math helper file to DMP6 example sketch
// - add Euler output and Yaw/Pitch/Roll output formats
// 2012-06-04 - remove accel offset clearing for better results (thanks Sungon Lee)
// 2012-06-01 - fixed gyro sensitivity to be 2000 deg/sec instead of 250
// 2012-05-30 - basic DMP initialization working
/* ============================================
I2Cdev device library code is placed under the MIT license
Copyright (c) 2012 Jeff Rowberg
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
THE SOFTWARE.
===============================================
*/
// I2Cdev and MPU6050 must be installed as libraries, or else the .cpp/.h files
// for both classes must be in the include path of your project
#include "I2Cdev.h"
#include "MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h"
//#include "MPU6050.h" // not necessary if using MotionApps include file
// Arduino Wire library is required if I2Cdev I2CDEV_ARDUINO_WIRE implementation
// is used in I2Cdev.h
#if I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_ARDUINO_WIRE
#include "Wire.h"
#endif
// class default I2C address is 0x68
// specific I2C addresses may be passed as a parameter here
// AD0 low = 0x68 (default for SparkFun breakout and InvenSense evaluation board)
// AD0 high = 0x69
MPU6050 mpu;
//MPU6050 mpu(0x69); // <-- use for AD0 high
/* =========================================================================
NOTE: In addition to connection 3.3v, GND, SDA, and SCL, this sketch
depends on the MPU-6050's INT pin being connected to the Arduino's
external interrupt #0 pin. On the Arduino Uno and Mega 2560, this is
digital I/O pin 2.
* ========================================================================= */
/* =========================================================================
NOTE: Arduino v1.0.1 with the Leonardo board generates a compile error
when using Serial.write(buf, len). The Teapot output uses this method.
The solution requires a modification to the Arduino USBAPI.h file, which
is fortunately simple, but annoying. This will be fixed in the next IDE
release. For more info, see these links:
http://arduino.cc/forum/index.php/topic,109987.0.html
http://code.google.com/p/arduino/issues/detail?id=958
* ========================================================================= */
// uncomment "OUTPUT_READABLE_QUATERNION" if you want to see the actual
// quaternion components in a [w, x, y, z] format (not best for parsing
// on a remote host such as Processing or something though)
//#define OUTPUT_READABLE_QUATERNION
// uncomment "OUTPUT_READABLE_EULER" if you want to see Euler angles
// (in degrees) calculated from the quaternions coming from the FIFO.
// Note that Euler angles suffer from gimbal lock (for more info, see
// http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gimbal_lock)
//#define OUTPUT_READABLE_EULER
// uncomment "OUTPUT_READABLE_YAWPITCHROLL" if you want to see the yaw/
// pitch/roll angles (in degrees) calculated from the quaternions coming
// from the FIFO. Note this also requires gravity vector calculations.
// Also note that yaw/pitch/roll angles suffer from gimbal lock (for
// more info, see: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gimbal_lock)
#define OUTPUT_READABLE_YAWPITCHROLL
// uncomment "OUTPUT_READABLE_REALACCEL" if you want to see acceleration
// components with gravity removed. This acceleration reference frame is
// not compensated for orientation, so +X is always +X according to the
// sensor, just without the effects of gravity. If you want acceleration
// compensated for orientation, us OUTPUT_READABLE_WORLDACCEL instead.
//#define OUTPUT_READABLE_REALACCEL
// uncomment "OUTPUT_READABLE_WORLDACCEL" if you want to see acceleration
// components with gravity removed and adjusted for the world frame of
// reference (yaw is relative to initial orientation, since no magnetometer
// is present in this case). Could be quite handy in some cases.
//#define OUTPUT_READABLE_WORLDACCEL
// uncomment "OUTPUT_TEAPOT" if you want output that matches the
// format used for the InvenSense teapot demo
//#define OUTPUT_TEAPOT
#define LED_PIN 13 // (Arduino is 13, Teensy is 11, Teensy++ is 6)
bool blinkState = false;
// MPU control/status vars
bool dmpReady = false; // set true if DMP init was successful
uint8_t mpuIntStatus; // holds actual interrupt status byte from MPU
uint8_t devStatus; // return status after each device operation (0 = success, !0 = error)
uint16_t packetSize; // expected DMP packet size (default is 42 bytes)
uint16_t fifoCount; // count of all bytes currently in FIFO
uint8_t fifoBuffer[64]; // FIFO storage buffer
// orientation/motion vars
Quaternion q; // [w, x, y, z] quaternion container
VectorInt16 aa; // [x, y, z] accel sensor measurements
VectorInt16 aaReal; // [x, y, z] gravity-free accel sensor measurements
VectorInt16 aaWorld; // [x, y, z] world-frame accel sensor measurements
VectorFloat gravity; // [x, y, z] gravity vector
float euler[3]; // [psi, theta, phi] Euler angle container
float ypr[3]; // [yaw, pitch, roll] yaw/pitch/roll container and gravity vector
// packet structure for InvenSense teapot demo
uint8_t teapotPacket[14] = { '$', 0x02, 0,0, 0,0, 0,0, 0,0, 0x00, 0x00, '\r', '\n' };
// ================================================================
// === INTERRUPT DETECTION ROUTINE ===
// ================================================================
volatile bool mpuInterrupt = false; // indicates whether MPU interrupt pin has gone high
void dmpDataReady() {
mpuInterrupt = true;
}
// ================================================================
// === INITIAL SETUP ===
// ================================================================
void setup() {
// join I2C bus (I2Cdev library doesn't do this automatically)
#if I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_ARDUINO_WIRE
Wire.begin();
TWBR = 24; // 400kHz I2C clock (200kHz if CPU is 8MHz)
#elif I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_BUILTIN_FASTWIRE
Fastwire::setup(400, true);
#endif
// initialize serial communication
// (115200 chosen because it is required for Teapot Demo output, but it's
// really up to you depending on your project)
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial); // wait for Leonardo enumeration, others continue immediately
// NOTE: 8MHz or slower host processors, like the Teensy @ 3.3v or Ardunio
// Pro Mini running at 3.3v, cannot handle this baud rate reliably due to
// the baud timing being too misaligned with processor ticks. You must use
// 38400 or slower in these cases, or use some kind of external separate
// crystal solution for the UART timer.
// initialize device
Serial.println(F("Initializing I2C devices..."));
mpu.initialize();
// verify connection
Serial.println(F("Testing device connections..."));
Serial.println(mpu.testConnection() ? F("MPU6050 connection successful") : F("MPU6050 connection failed"));
// wait for ready
Serial.println(F("\nSend any character to begin DMP programming and demo: "));
while (Serial.available() && Serial.read()); // empty buffer
while (!Serial.available()); // wait for data
while (Serial.available() && Serial.read()); // empty buffer again
// load and configure the DMP
Serial.println(F("Initializing DMP..."));
devStatus = mpu.dmpInitialize();
// supply your own gyro offsets here, scaled for min sensitivity
mpu.setXGyroOffset(220);
mpu.setYGyroOffset(76);
mpu.setZGyroOffset(-85);
mpu.setZAccelOffset(1788); // 1688 factory default for my test chip
// make sure it worked (returns 0 if so)
if (devStatus == 0) {
// turn on the DMP, now that it's ready
Serial.println(F("Enabling DMP..."));
mpu.setDMPEnabled(true);
// enable Arduino interrupt detection
Serial.println(F("Enabling interrupt detection (Arduino external interrupt 0)..."));
attachInterrupt(0, dmpDataReady, RISING);
mpuIntStatus = mpu.getIntStatus();
// set our DMP Ready flag so the main loop() function knows it's okay to use it
Serial.println(F("DMP ready! Waiting for first interrupt..."));
dmpReady = true;
// get expected DMP packet size for later comparison
packetSize = mpu.dmpGetFIFOPacketSize();
} else {
// ERROR!
// 1 = initial memory load failed
// 2 = DMP configuration updates failed
// (if it's going to break, usually the code will be 1)
Serial.print(F("DMP Initialization failed (code "));
Serial.print(devStatus);
Serial.println(F(")"));
}
// configure LED for output
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
}
// ================================================================
// === MAIN PROGRAM LOOP ===
// ================================================================
void loop() {
// if programming failed, don't try to do anything
if (!dmpReady) return;
// wait for MPU interrupt or extra packet(s) available
while (!mpuInterrupt && fifoCount < packetSize) {
// other program behavior stuff here
// .
// .
// .
// if you are really paranoid you can frequently test in between other
// stuff to see if mpuInterrupt is true, and if so, "break;" from the
// while() loop to immediately process the MPU data
// .
// .
// .
}
// reset interrupt flag and get INT_STATUS byte
mpuInterrupt = false;
mpuIntStatus = mpu.getIntStatus();
// get current FIFO count
fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount();
// check for overflow (this should never happen unless our code is too inefficient)
if ((mpuIntStatus & 0x10) || fifoCount == 1024) {
// reset so we can continue cleanly
mpu.resetFIFO();
Serial.println(F("FIFO overflow!"));
// otherwise, check for DMP data ready interrupt (this should happen frequently)
} else if (mpuIntStatus & 0x02) {
// wait for correct available data length, should be a VERY short wait
while (fifoCount < packetSize) fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount();
// read a packet from FIFO
mpu.getFIFOBytes(fifoBuffer, packetSize);
// track FIFO count here in case there is > 1 packet available
// (this lets us immediately read more without waiting for an interrupt)
fifoCount -= packetSize;
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_QUATERNION
// display quaternion values in easy matrix form: w x y z
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
Serial.print("quat\t");
Serial.print(q.w);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(q.x);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(q.y);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.println(q.z);
#endif
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_EULER
// display Euler angles in degrees
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetEuler(euler, &q);
Serial.print("euler\t");
Serial.print(euler[0] * 180/M_PI);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(euler[1] * 180/M_PI);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.println(euler[2] * 180/M_PI);
#endif
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_YAWPITCHROLL
// display Euler angles in degrees
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetGravity(&gravity, &q);
mpu.dmpGetYawPitchRoll(ypr, &q, &gravity);
Serial.print("ypr\t");
Serial.print(ypr[0] * 180/M_PI);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(ypr[1] * 180/M_PI);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.println(ypr[2] * 180/M_PI);
#endif
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_REALACCEL
// display real acceleration, adjusted to remove gravity
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetAccel(&aa, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetGravity(&gravity, &q);
mpu.dmpGetLinearAccel(&aaReal, &aa, &gravity);
Serial.print("areal\t");
Serial.print(aaReal.x);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(aaReal.y);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.println(aaReal.z);
#endif
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_WORLDACCEL
// display initial world-frame acceleration, adjusted to remove gravity
// and rotated based on known orientation from quaternion
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetAccel(&aa, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetGravity(&gravity, &q);
mpu.dmpGetLinearAccel(&aaReal, &aa, &gravity);
mpu.dmpGetLinearAccelInWorld(&aaWorld, &aaReal, &q);
Serial.print("aworld\t");
Serial.print(aaWorld.x);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(aaWorld.y);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.println(aaWorld.z);
#endif
#ifdef OUTPUT_TEAPOT
// display quaternion values in InvenSense Teapot demo format:
teapotPacket[2] = fifoBuffer[0];
teapotPacket[3] = fifoBuffer[1];
teapotPacket[4] = fifoBuffer[4];
teapotPacket[5] = fifoBuffer[5];
teapotPacket[6] = fifoBuffer[8];
teapotPacket[7] = fifoBuffer[9];
teapotPacket[8] = fifoBuffer[12];
teapotPacket[9] = fifoBuffer[13];
Serial.write(teapotPacket, 14);
teapotPacket[11]++; // packetCount, loops at 0xFF on purpose
#endif
// blink LED to indicate activity
blinkState = !blinkState;
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, blinkState);
}
}
일단 아두이노ide example에서 보이지는않지만
빌드는 정상적으로 된다.
그런데 위 코드에서 인터럽트핀을 내가 D2가 아닌 D4를 써서 좀바꿔주고 싶은데
어디있는지 잘안보인다.
일단 필요한 lib 가져오고
i2c 통신 설정하는 내용이 앞에나온다.
// I2Cdev and MPU6050 must be installed as libraries, or else the .cpp/.h files
// for both classes must be in the include path of your project
#include "I2Cdev.h"
#include "MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h"
//#include "MPU6050.h" // not necessary if using MotionApps include file
// Arduino Wire library is required if I2Cdev I2CDEV_ARDUINO_WIRE implementation
// is used in I2Cdev.h
#if I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_ARDUINO_WIRE
#include "Wire.h"
#endif
// class default I2C address is 0x68
// specific I2C addresses may be passed as a parameter here
// AD0 low = 0x68 (default for SparkFun breakout and InvenSense evaluation board)
// AD0 high = 0x69
MPU6050 mpu;
//MPU6050 mpu(0x69); // <-- use for AD0 high
근데 다음 내용이 문제다.
인터럽트 핀을 우노보드에서 d2로 연결해야한다고 하는데
나는 d4를 쓴다.
/* =========================================================================
NOTE: In addition to connection 3.3v, GND, SDA, and SCL, this sketch
depends on the MPU-6050's INT pin being connected to the Arduino's
external interrupt #0 pin. On the Arduino Uno and Mega 2560, this is
digital I/O pin 2.
* ========================================================================= */
일단 gpt 한태 질문
q : 아두이노 우노보드 mpu6050 사용하는데 INT핀을 우노보드의 D2에다가 연결하라고 해 다른 핀을 사용하면 안될까?
a : 다른 핀을 사용할 수도 있지만, MPU6050의 INT 핀은 보통 D2 핀에 연결하는 것을 권장합니다. 이는 MPU6050 라이브러리와 관련된 코드가 기본적으로 D2 핀을 사용하기 때문입니다. 만약 다른 핀을 사용하려면 해당 핀의 인터럽트 기능을 사용할 수 있는지 확인하고, 코드를 수정하여 새로운 핀을 사용하도록 설정해야 합니다.
q : 그러면 mpu6050 여러개 사용하는 경우 int핀들을 전부 d2와 연결해야되??
a : MPU6050 여러 개를 사용하는 경우, 각 MPU6050의 INT 핀을 모두 하나의 핀(D2)에 연결할 필요는 없습니다. 각 MPU6050의 INT 핀을 서로 다른 디지털 핀에 연결하여 각각의 MPU6050의 인터럽트 신호를 처리할 수 있습니다. 따라서 각 MPU6050 모듈의 INT 핀을 서로 다른 디지털 핀에 연결하여 사용하면 됩니다.
q : 그러면 나는 mpu6050 인터럽트핀을 우노보드 d4에 연결해서 사용하면 mpu6050 헤더파일은 변경하면되는거야? 어떻게 고치면되?
a : 네, MPU6050의 INT 핀을 우노보드의 D4에 연결한 경우 MPU6050 라이브러리의 헤더 파일을 수정하여 해당 핀을 사용하도록 변경해야 합니다.
라이브러리의 소스 코드를 열어 해당 핀을 수정하거나, 라이브러리의 설정 파일에서 해당 핀을 재정의할 수 있습니다. 보통 라이브러리에는 핀 매핑에 대한 설정이 있으므로 해당 설정을 변경하여 INT 핀을 D4로 사용할 수 있습니다.
핀 매핑 설정을 찾아 해당 핀을 D4로 수정하고, 라이브러리를 다시 컴파일하여 사용하면 MPU6050의 INT 핀을 D4에 연결하여 정상적으로 사용할 수 있습니다.
gpt 설명만 보면 mpu 6050 여러개 쓰면 int핀도 따로해줘야한다고 하는데
int를 안써도 되나 싶어서 찾아보다
발견한 글 여기서는 결론은 인터럽트 핀은 옵션이란다.
https://arduino.stackexchange.com/questions/44937/how-important-is-the-int-pin-of-the-mpu6050-gy-521
How important is the INT pin of the MPU6050 (GY-521)?
I want to wire multiple MPU6050 (at least 16 of them) to an arduino UNO for development (then nano for production). So I first started wiring one MPU6050 to an arduino like shown on the diyhacking
arduino.stackexchange.com
다시 gpt 질문
q : mpu 6050에서 인터럽트핀이 언제사용되 우노보드랑 연결해서쓰려고해
a : MPU6050의 인터럽트 핀은 다양한 용도로 사용될 수 있습니다. 일반적으로 MPU6050에서 인터럽트 핀은 다음과 같은 상황에서 사용됩니다:
1. Motion Detection(동작 감지): MPU6050은 움직임을 감지하는 기능을 제공합니다. 인터럽트 핀을 사용하여 특정 동작이 감지되었을 때, 우노보드에 인터럽트 신호를 보내고 처리할 수 있습니다.
2. Freefall Detection(자유 낙하 감지): MPU6050은 자유 낙하를 감지할 수 있는 기능도 제공합니다. 인터럽트 핀을 사용하여 자유 낙하 감지 시 우노보드에 알림을 보낼 수 있습니다.
3. Orientation Tracking(자세 추적): MPU6050은 자세 추적을 위한 기능도 갖추고 있습니다. 인터럽트 핀을 사용하여 특정 자세 조건이 충족되었을 때, 우노보드에 인터럽트를 발생시키고 처리할 수 있습니다.
따라서, MPU6050의 인터럽트 핀을 우노보드와 연결하여 사용하면 이러한 기능들을 활용할 수 있습니다. 사용하고자 하는 기능에 따라 MPU6050 라이브러리와 우노보드 코드를 적절하게 설정 및 프로그래밍해야 합니다.
이 내용만 보면 인터럽트 쓰긴해야될것같은데
다른글 찾아봄
이 글에서 설명하는 예제가 2가지가 있는데
첫 예제에서는 INT핀안쓰고
둘째 예제에서는 INT핀 사용
https://www.jkelec.co.kr/img/sensors/manual/mpu6050_gy521/mpu6050_gy521_manual.html
MPU6050 GY-521 센서 메뉴얼
1. MPU6050 센서 소개 MPU6050은 가속도와 자이로센서가 1개의 센서에 모두 포함하고 있는 6DOF(Degrees of Freedom) 센서이다. MPU6050은 I2C (Inter Integrated Circuit) 통신 프로토콜을 통해서 데이터를 추출 할
www.jkelec.co.kr
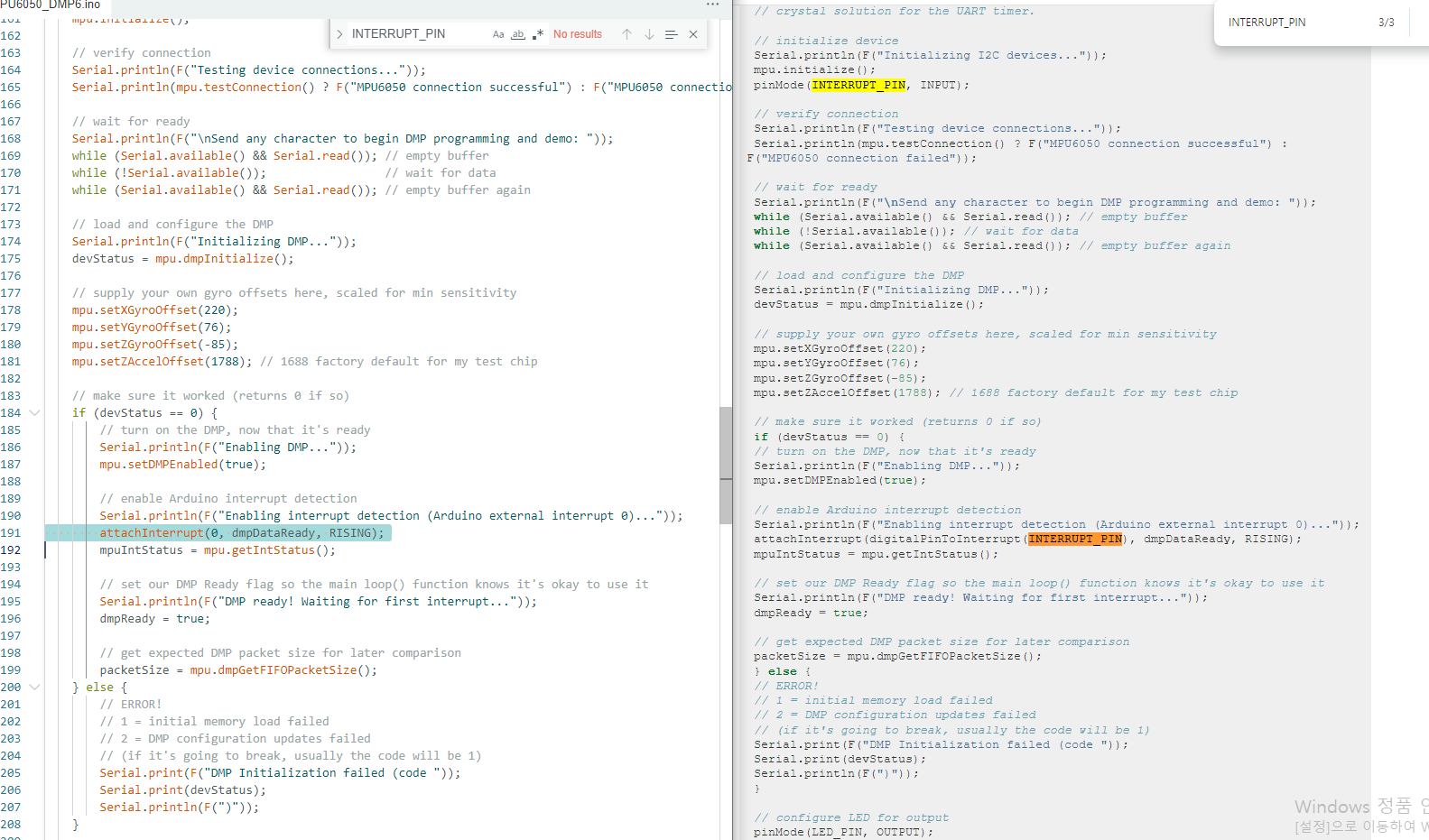
그런데 둘째 예재를 보면 인터럽트 핀을 지정하는 내용이 나온다.

내가 다운받은 예제 코드랑 여기서 설명하는 예제비교해보자
거의 비슷하긴한데 우측코드는
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(INTERRUPT_PIN), dmpDataReady, RISING);
좌측코드는
약간 차이난다.
일단 mpu6050 여러개 받아오는건 나중에 생각하고
내가 갖고 있는 예제코드만 인터럽트핀 D4로 바꿔서 동작하도록 고침
변경된건 인터럽트핀 정의해서
어태치 인터럽트한것정도?
#define INTERRUPT_PIN 4 // use pin 2 on Arduino Uno & most boards
void setup() {
// join I2C bus (I2Cdev library doesn't do this automatically)
#if I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_ARDUINO_WIRE
Wire.begin();
TWBR = 24; // 400kHz I2C clock (200kHz if CPU is 8MHz)
#elif I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_BUILTIN_FASTWIRE
Fastwire::setup(400, true);
#endif
// initialize serial communication
// (115200 chosen because it is required for Teapot Demo output, but it's
// really up to you depending on your project)
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial); // wait for Leonardo enumeration, others continue immediately
// NOTE: 8MHz or slower host processors, like the Teensy @ 3.3v or Ardunio
// Pro Mini running at 3.3v, cannot handle this baud rate reliably due to
// the baud timing being too misaligned with processor ticks. You must use
// 38400 or slower in these cases, or use some kind of external separate
// crystal solution for the UART timer.
// initialize device
Serial.println(F("Initializing I2C devices..."));
mpu.initialize();
pinMode(INTERRUPT_PIN, INPUT);
// verify connection
Serial.println(F("Testing device connections..."));
Serial.println(mpu.testConnection() ? F("MPU6050 connection successful") : F("MPU6050 connection failed"));
// wait for ready
Serial.println(F("\nSend any character to begin DMP programming and demo: "));
while (Serial.available() && Serial.read()); // empty buffer
while (!Serial.available()); // wait for data
while (Serial.available() && Serial.read()); // empty buffer again
// load and configure the DMP
Serial.println(F("Initializing DMP..."));
devStatus = mpu.dmpInitialize();
// supply your own gyro offsets here, scaled for min sensitivity
mpu.setXGyroOffset(220);
mpu.setYGyroOffset(76);
mpu.setZGyroOffset(-85);
mpu.setZAccelOffset(1788); // 1688 factory default for my test chip
// make sure it worked (returns 0 if so)
if (devStatus == 0) {
// turn on the DMP, now that it's ready
Serial.println(F("Enabling DMP..."));
mpu.setDMPEnabled(true);
// enable Arduino interrupt detection
Serial.println(F("Enabling interrupt detection (Arduino external interrupt 0)..."));
//attachInterrupt(0, dmpDataReady, RISING);
attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(INTERRUPT_PIN), dmpDataReady, RISING);
mpuIntStatus = mpu.getIntStatus();
// set our DMP Ready flag so the main loop() function knows it's okay to use it
Serial.println(F("DMP ready! Waiting for first interrupt..."));
dmpReady = true;
// get expected DMP packet size for later comparison
packetSize = mpu.dmpGetFIFOPacketSize();
} else {
// ERROR!
// 1 = initial memory load failed
// 2 = DMP configuration updates failed
// (if it's going to break, usually the code will be 1)
Serial.print(F("DMP Initialization failed (code "));
Serial.print(devStatus);
Serial.println(F(")"));
}
// configure LED for output
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
}
업로드 했지만 동작이 안된다
DMP ready! Waiting for first interrupt...
원래대로 고치고 핀도 d2로 옮기니 정상동작 확인
어카지 인터럽트핀 여러개해야하는데
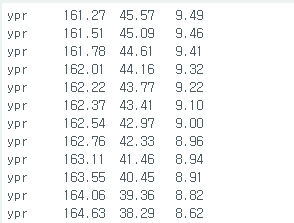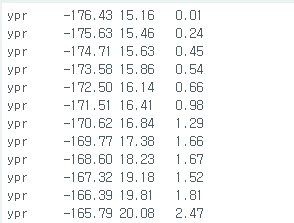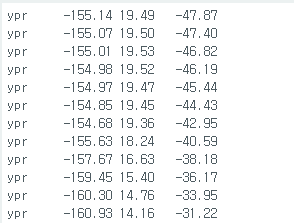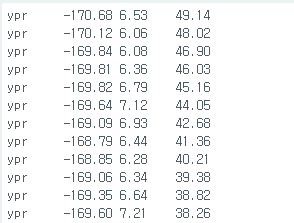
근데 코드안고치고 인터럽트핀 아얘 뽑아도 정상적으로 동작한다.
괜한 걱정한듯
하지만 초기화 부분에서 자꾸 멈춰서 주석처리시켜줘야할듯
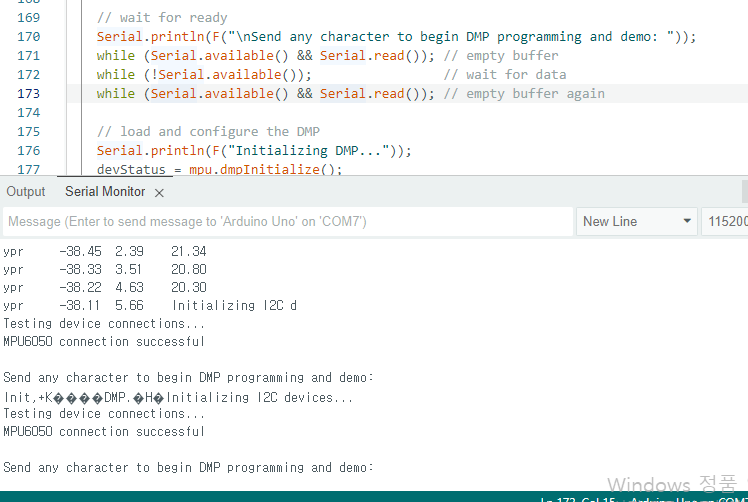
근대 실행시키고나서 보면 yaw가 계속 누적되서 커지다가 어느순간 멈춘다.
ok 기존 코드는 너무 길어서
주석이나 몇가지 부분들을 빼서 조금 줄임
일단. 인터럽트 핀 안쓰고 ypr 받아오도록 정리
#include "I2Cdev.h"
#include "MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h"
//#include "MPU6050.h" // not necessary if using MotionApps include file
// Arduino Wire library is required if I2Cdev I2CDEV_ARDUINO_WIRE implementation
// is used in I2Cdev.h
#if I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_ARDUINO_WIRE
#include "Wire.h"
#endif
// class default I2C address is 0x68
// specific I2C addresses may be passed as a parameter here
// AD0 low = 0x68 (default for SparkFun breakout and InvenSense evaluation board)
// AD0 high = 0x69
MPU6050 mpu;
//MPU6050 mpu(0x69); // <-- use for AD0 high
#define OUTPUT_READABLE_YAWPITCHROLL
#define LED_PIN 13 // (Arduino is 13, Teensy is 11, Teensy++ is 6)
bool blinkState = false;
// MPU control/status vars
bool dmpReady = false; // set true if DMP init was successful
uint8_t mpuIntStatus; // holds actual interrupt status byte from MPU
uint8_t devStatus; // return status after each device operation (0 = success, !0 = error)
uint16_t packetSize; // expected DMP packet size (default is 42 bytes)
uint16_t fifoCount; // count of all bytes currently in FIFO
uint8_t fifoBuffer[64]; // FIFO storage buffer
// orientation/motion vars
Quaternion q; // [w, x, y, z] quaternion container
VectorInt16 aa; // [x, y, z] accel sensor measurements
VectorInt16 aaReal; // [x, y, z] gravity-free accel sensor measurements
VectorInt16 aaWorld; // [x, y, z] world-frame accel sensor measurements
VectorFloat gravity; // [x, y, z] gravity vector
float euler[3]; // [psi, theta, phi] Euler angle container
float ypr[3]; // [yaw, pitch, roll] yaw/pitch/roll container and gravity vector
// packet structure for InvenSense teapot demo
uint8_t teapotPacket[14] = { '$', 0x02, 0,0, 0,0, 0,0, 0,0, 0x00, 0x00, '\r', '\n' };
volatile bool mpuInterrupt = false; // indicates whether MPU interrupt pin has gone high
void dmpDataReady() {
mpuInterrupt = true;
}
void setup() {
// join I2C bus (I2Cdev library doesn't do this automatically)
#if I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_ARDUINO_WIRE
Wire.begin();
TWBR = 24; // 400kHz I2C clock (200kHz if CPU is 8MHz)
#elif I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_BUILTIN_FASTWIRE
Fastwire::setup(400, true);
#endif
// initialize serial communication
// (115200 chosen because it is required for Teapot Demo output, but it's
// really up to you depending on your project)
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial); // wait for Leonardo enumeration, others continue immediately
// initialize device
Serial.println(F("Initializing I2C devices..."));
mpu.initialize();
//pinMode(INTERRUPT_PIN, INPUT);
// verify connection
Serial.println(F("Testing device connections..."));
Serial.println(mpu.testConnection() ? F("MPU6050 connection successful") : F("MPU6050 connection failed"));
// wait for ready
/*
Serial.println(F("\nSend any character to begin DMP programming and demo: "));
while (Serial.available() && Serial.read()); // empty buffer
while (!Serial.available()); // wait for data
while (Serial.available() && Serial.read()); // empty buffer again
*/
// load and configure the DMP
Serial.println(F("Initializing DMP..."));
devStatus = mpu.dmpInitialize();
// supply your own gyro offsets here, scaled for min sensitivity
mpu.setXGyroOffset(220);
mpu.setYGyroOffset(76);
mpu.setZGyroOffset(-85);
mpu.setZAccelOffset(1788); // 1688 factory default for my test chip
// make sure it worked (returns 0 if so)
if (devStatus == 0) {
// turn on the DMP, now that it's ready
Serial.println(F("Enabling DMP..."));
mpu.setDMPEnabled(true);
// enable Arduino interrupt detection
Serial.println(F("Enabling interrupt detection (Arduino external interrupt 0)..."));
attachInterrupt(0, dmpDataReady, RISING);
//attachInterrupt(digitalPinToInterrupt(INTERRUPT_PIN), dmpDataReady, RISING);
mpuIntStatus = mpu.getIntStatus();
// set our DMP Ready flag so the main loop() function knows it's okay to use it
Serial.println(F("DMP ready! Waiting for first interrupt..."));
dmpReady = true;
// get expected DMP packet size for later comparison
packetSize = mpu.dmpGetFIFOPacketSize();
} else {
// ERROR!
// 1 = initial memory load failed
// 2 = DMP configuration updates failed
// (if it's going to break, usually the code will be 1)
Serial.print(F("DMP Initialization failed (code "));
Serial.print(devStatus);
Serial.println(F(")"));
}
// configure LED for output
pinMode(LED_PIN, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
// if programming failed, don't try to do anything
if (!dmpReady) return;
// wait for MPU interrupt or extra packet(s) available
while (!mpuInterrupt && fifoCount < packetSize) {
}
// reset interrupt flag and get INT_STATUS byte
mpuInterrupt = false;
mpuIntStatus = mpu.getIntStatus();
// get current FIFO count
fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount();
// check for overflow (this should never happen unless our code is too inefficient)
if ((mpuIntStatus & 0x10) || fifoCount == 1024) {
// reset so we can continue cleanly
mpu.resetFIFO();
Serial.println(F("FIFO overflow!"));
// otherwise, check for DMP data ready interrupt (this should happen frequently)
} else if (mpuIntStatus & 0x02) {
// wait for correct available data length, should be a VERY short wait
while (fifoCount < packetSize) fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount();
// read a packet from FIFO
mpu.getFIFOBytes(fifoBuffer, packetSize);
// track FIFO count here in case there is > 1 packet available
// (this lets us immediately read more without waiting for an interrupt)
fifoCount -= packetSize;
#ifdef OUTPUT_READABLE_YAWPITCHROLL
// display Euler angles in degrees
mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer);
mpu.dmpGetGravity(&gravity, &q);
mpu.dmpGetYawPitchRoll(ypr, &q, &gravity);
Serial.print("ypr\t");
Serial.print(ypr[0] * 180/M_PI);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.print(ypr[1] * 180/M_PI);
Serial.print("\t");
Serial.println(ypr[2] * 180/M_PI);
#endif
// blink LED to indicate activity
blinkState = !blinkState;
digitalWrite(LED_PIN, blinkState);
}
}
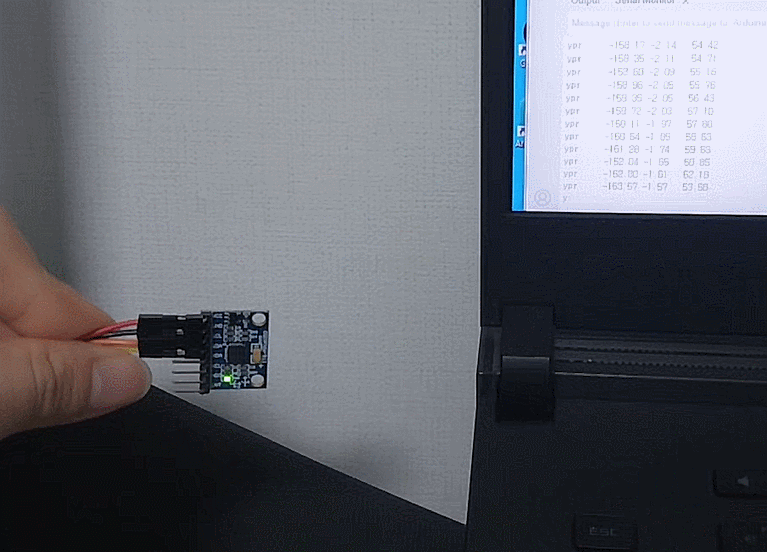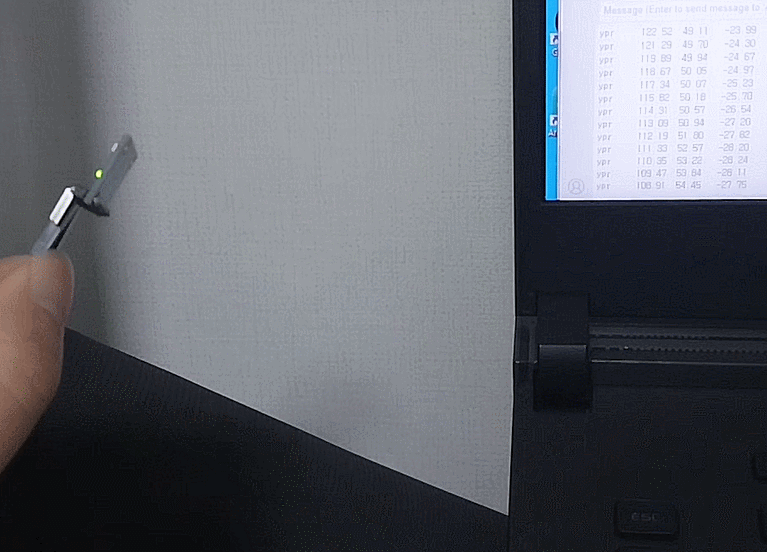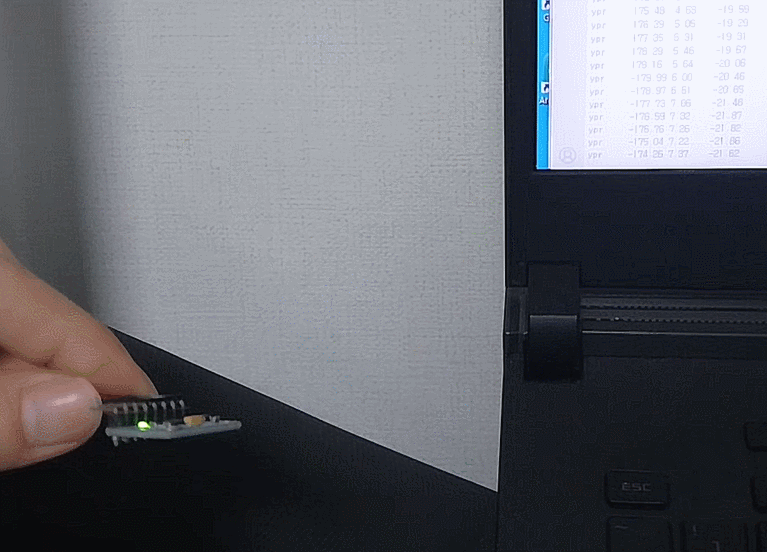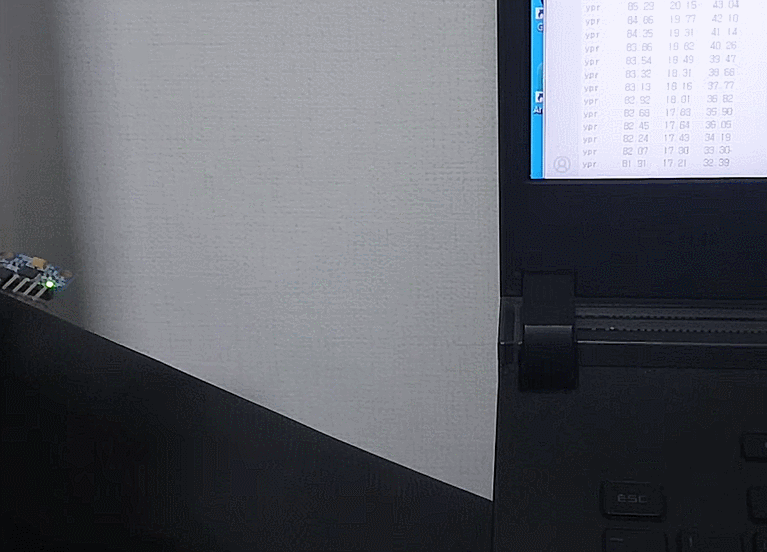
촬영 결과
대충 되긴한다
프레임은 줄인다고 22뿐인데 이미지가 커서 용량이꽤되네
'컴퓨터과학 > 언리얼' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 관성모션 - 6. mpu6050 ypr 블루투스로 언리얼에서 받기(받긴한데) (0) | 2024.02.22 |
|---|---|
| 관성모션 - 5. 블루투스로 MPU6050 YPR 보내기 (0) | 2024.02.22 |
| 언리얼 했던것들 (0) | 2024.02.21 |
| 관성모션 - 3. 언리얼PC와 아두이노 블루투스 통신 (0) | 2024.02.14 |
| 관성모션 - 2. 블루투스 기초통신 (0) | 2024.02.14 |